Views: 0 Author: Danny Publish Time: 2026-01-16 Origin: Site








ABS injection molding is a common plastic manufacturing process. It involves injecting molten ABS plastic into a mold cavity under high temperature and pressure to create various plastic parts and products used in everyday life. In this article, you will learn everything about ABS injection molding, including its definition, advantages and disadvantages, applications, process, design considerations and common challenges & solutions.
| Table of Contents |
1.What is ABS Injection Molding? |
2. Why Is ABS Used in Injection Molding? |
3. What Are the Advantages of ABS Injection Molding? |
4. What Are the Disadvantages of ABS Injection Molding? |
5. What Are Some Common Applications of ABS Plastic Molding? |
6. ABS Plastic Injection Molding Process |
7. ABS Plastic Injection Molding Design Guidelines |
8. Common Challenges and Solutions in ABS Injection Molding |
9. Conclusion |
| 10.FAQ |
ABS injection molding is a process where ABS plastic pellets are heated to a molten state in an injection molding machine, then injected at high speed into a plastic injection mold tooling. After cooling and solidification, the part is demolded, allowing for the mass production of plastic parts with consistent dimensions.
Thermoplastics are widely used in the manufacture of various plastic parts and products. Among the many thermoplastic materials, ABS (acrylonitrile-butadiene-styrene) stands out due to its high impact resistance, excellent mechanical strength, outstanding chemical resistance, long-term durability, and low cost, making it one of the most widely used materials in plastic injection molding. ABS achieves an optimal balance of strength, durability, and processability by combining three key monomers:
Acrylonitrile (15%-35%) → Enhances chemical & heat resistance
Butadiene (5%-30%) → Boosts impact strength & toughness
Styrene (40%-60%) → Improves rigidity & surface finish
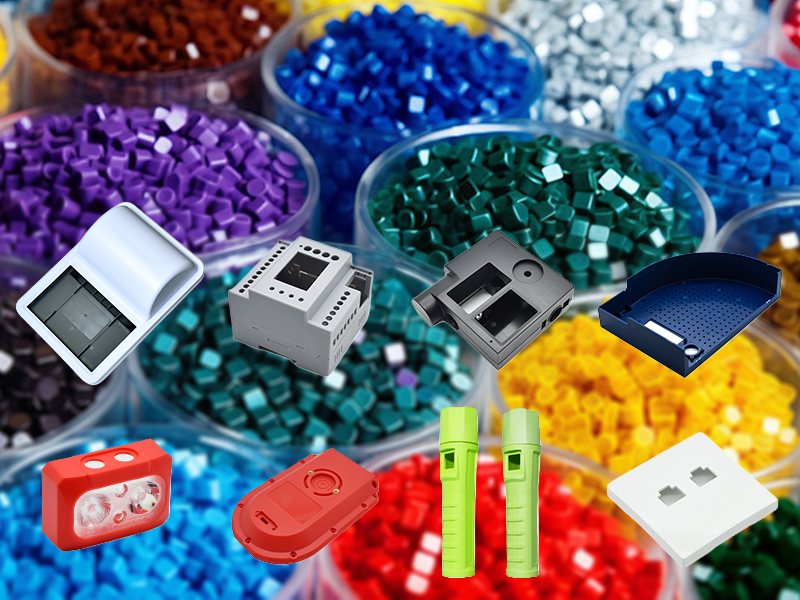

ABS offers excellent impact resistance and mechanical strength. After injection molding processing, it produces highly durable injection-molded parts.
ABS Plastic possesses excellent impact resistance, with a notched impact strength of 10-20 ft-lbs/in, enabling ABS injection-molded parts to withstand drops, vibrations, and harsh environments, thus ensuring a longer product lifespan.
Furthermore, ABS exhibits good overall mechanical strength, with an elastic modulus of approximately 2.3-2.8 GPa. Therefore, ABS injection molding is well-suited for structural and load-bearing components.
ABS injection molding offers significant price advantages, primarily due to the combined factors of materials, molds, processes, and mass production.
Materials:ABS is a general-purpose engineering plastic with high global production volume and a mature supply chain. The raw material price is stable and very low, approximately $1 to $3 per kilogram.
Molds:ABS requires less demanding mold steel, resulting in less mold wear, lower maintenance costs, and controllable mold investment costs, leading to lower long-term per-unit costs.
Processes:ABS has good fluidity, making mold filling easy and injection molding stable with short cycle times, resulting in high production efficiency and effectively reducing machine and labor costs.
Mass Production: ABS has a low shrinkage rate (approximately 0.4–0.7%), leading to a high yield rate in mass production and good dimensional stability, effectively reducing the cost per unit.
ABS injection molding is easy to post-process, which is determined by its material structure, surface characteristics, and thermal properties.
ABS contains a butadiene rubber phase, has high surface polarity and good adhesion. After ABS injection molding, the product surface has a fine structure, making it easy to paint, electroplate, screen print, and pad print.
ABS material has moderate hardness. After ABS injection molding, the product surface is less prone to burrs or cracks, making it suitable for laser processing.
ABS has a moderate heat distortion temperature (85–105°C). After ABS injection molding, the stress distribution is uniform, making it suitable for ultrasonic welding.
ABS has a relatively low heat distortion temperature (HDT), typically around 90°C (194°F). Therefore, ABS injection parts are not suitable for applications requiring prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
ABS injection molded parts are not resistant to ultraviolet (UV) light and are prone to discoloration and aging with prolonged outdoor use. For outdoor applications, materials such as UV-stabilized ABS, ASA, or ASA/PC are usually required.
ABS plastic, with its excellent mechanical properties and processing versatility, is an ideal choice for numerous industries. The table below shows some common applications of ABS injection molding.
Industry |
Specific Product Examples |
Reasons for Application |
Consumer Electronics |
Remote control casings, router casings, speaker casings, charger casings, set-top box casings |
Good appearance, dimensional stability, easy to paint |
Home Appliances |
Rice cooker casings, vacuum cleaner casings, coffee machine casings, air purifier casings, electric fan casings |
Stable molding, impact resistance, controllable cost |
Smart Home |
Smart switch panel casings, thermostat casings, smart lock casings, sensor casings, water filter casings |
High aesthetic requirements, good assembly precision |
Medical |
Blood glucose meter casings, electrocardiogram monitor casings, blood analyzer casings, nebulizer casings |
Dimensional stability, low mass production cost |
Automotive |
Center console panel casings, instrument panel covers, air vent casings, car button casings, armrest box casings |
Good surface quality, dimensional stability |
Security |
Fire alarm covers, access control equipment casings, walkie-talkie casings, control console casings, surveillance camera casings |
Impact resistance, easy secondary processing |
Industrial Control |
Control box casings, power supply casings, instrument casings, PLC casings, power distribution module casings |
Easy processing, high cost-effectiveness |
Toys & Daily Necessities |
Toy casings, tool handle casings, storage box casings, game console casings, daily appliance casings |
Easy to color, low mass production cost |

Firefighter Light Housings

Fire Alarm Covers
ABS is also suitable for injection molding of special blends such as PC/ABS, ABS/PA, ABS/PBT, and flame-retardant ABS, to meet customers' unique performance requirements.
The ABS injection molding process includes the following main steps:
ABS pellets need to be dried before injection molding to remove moisture. ABS is hygroscopic, and insufficient drying can lead to defects such as air bubbles during the molding process.
Typical drying conditions for ABS pellets are 2-4 hours or longer at a temperature of 80-95 °C to achieve the target moisture content.
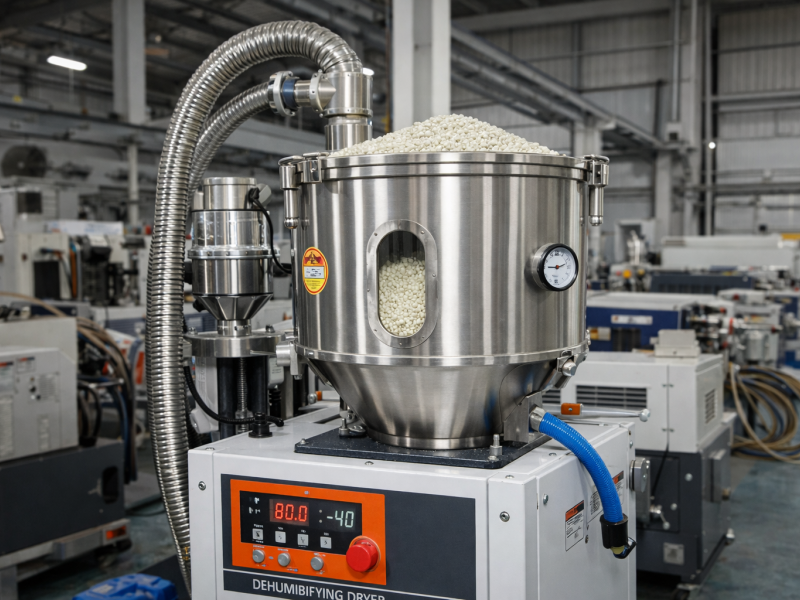

The dried ABS pellets are fed into the hopper of the injection molding machine and then into the heated barrel.
The ABS pellets melt into a viscous fluid in the heated barrel. The barrel temperature is generally controlled at 200-250°C, depending on the material grade.
When the molten ABS accumulates to the set amount in the barrel, the injection molding machine enters the injection phase. At this time, the screw (or plunger) stably injects the melt into the mold cavity under high pressure.
Step4: Cooling / Solidification
After injection, the molten ABS must cool and solidify into the shape of the mold cavity.
The mold usually has cooling channels to regulate the temperature and accelerate cooling.
After sufficient cooling, the mold opens. Then ejector pins push the solidified part out.
Proper design (such as a reasonable draft angle) facilitates the smooth demolding of the solidified part.
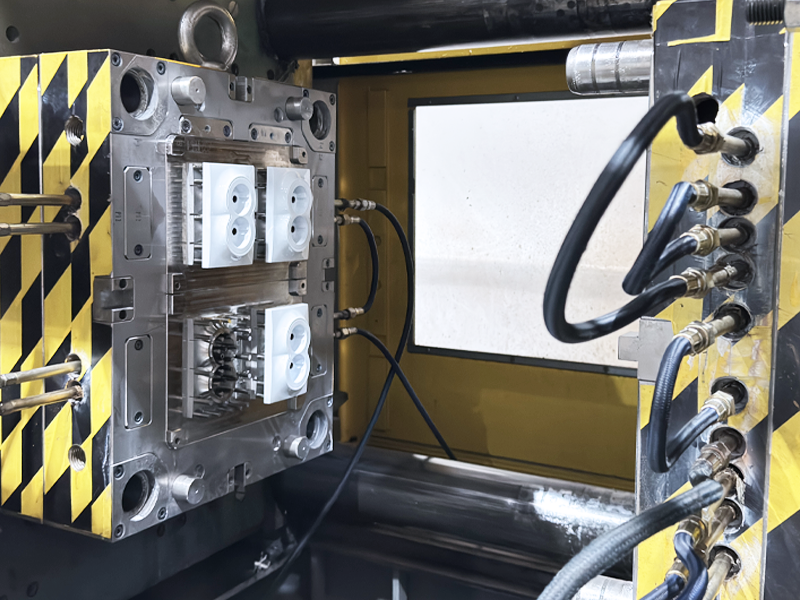
After the part is ejected, it may require trimming (removing gates, runners, or flash).
Other processes may also be needed, including post-processing (such as electroplating, painting) or assembly.
These steps (Melting, Injection, Cooling, and Ejection) form the abs injection molding cycle , which repeats rapidly for high-volume production.

7.1 Optimizing Wall Thickness
For optimal performance and ease of manufacturing, ensure that the wall thickness of ABS parts stays between 0.045” and 0.140” (1.14 to 3.56 mm). Consistency in wall thickness is crucial to avoid issues like warping, sink marks, and uneven cooling. Avoid abrupt thickness variations between adjacent walls to improve material flow and part integrity.
Ensure proper draft angles between 0.5° and 1° on vertical surfaces to facilitate smooth part ejection from the mold. Insufficient draft can cause parts to stick to the mold, increasing the risk of defects and tooling damage. Adequate draft angles also help reduce friction, which improves mold longevity and cycle times.
Avoid sharp corners in ABS parts to reduce stress concentrations. A minimum radius of 25% of the wall thickness is recommended, and for maximum strength, use a radius equal to 60% of the wall thickness. This improves part durability, material flow, and moldability during the injection process.

For ABS injection molding, part tolerances are divided into commercial and fine categories. For parts under 160 mm, commercial tolerances range from 0.1 to 0.325 mm. For smaller parts (≤ 100 mm), fine tolerances of 0.050 to 0.1 mm are achievable. Design with realistic tolerance requirements to avoid unnecessary adjustments and costs.
Undercuts can complicate the mold design and increase costs, as they may require special tooling or slides. Where possible, design parts to minimize undercuts, or use core pins and slides for complex geometries. This simplifies mold manufacturing and ensures smoother, more efficient production.
8. Common Challenges and Solutions in ABS Injection Molding
The table below shows some common challenges and solutions in ABS injection molding processing:
Common Challenges |
Solutions |
Difficulty in demolding the product |
|
Poor product dimensional stability |
|
Product warping and deformation |
|
Product sink marks |
|
Surface silver streaks/air bubble |
|

Deformation

Sink Marks
9. Conclusion
All in all, this article covers everything about ABS injection molding—including its definition, properties, applications, process, design considerations, common challenges and solutions. With its outstanding impact resistance, mechanical strength, cost-effectiveness, and ease of post-processing, ABS injection molding is widely used in producing electrical enclosures, smart home devices, medical casings, appliance housings, and more.
Whether you need precision molds or large-scale production of ABS parts, selecting an experienced injection molding manufacturer like Alpine Mold is crucial to the success of your ABS injection molding project. With 24 years of injection molding expertise and over 10,000 successfully completed projects, Alpine Mold can help you achieve stable, efficient mass production while ensuring product quality. If you need plastic injection molding tools or injection molding services, feel free to send us your 3D drawings for a quote!
Yes,because ABS is a thermoplastic material, clean industrial ABS waste can be melted and reprocessed.
No. ABS is recyclable, but not 100% recyclable.
ABS waste containing contaminants such as paint, metal inserts, and mixed plastics cannot be recycled.
Because they will leave behind impurity particles after being crushed and melted, leading to many molding defects when reused.
No. Standard ABS has a heat deflection temperature of around 90°C 。
For higher temperature or outdoor applications, ASA, PC, PPS, PC+GF, PEEK plastic are recommended.
The biggest difference between ABS and ASA lies in their weather resistance and UV resistance.
ABS has poor weather resistance and UV resistance; ABS injection molded parts tend to become brittle and age easily when exposed to sunlight for extended periods.
ASA has excellent weather resistance and UV resistance; ASA injection molded parts do not fade or age even after prolonged exposure to sunlight outdoors.
Therefore, ABS is very suitable for producing indoor products, while ASA is ideal for producing outdoor products during injection molding processes.
Before choosing the appropriate ABS granule grade, you must first clarify the performance requirements of your project.
1. If you are looking for a cost-effective solution and require good rigidity and toughness, we recommend choosing the general-purpose grade. This material is suitable for manufacturing most electronic casings and daily necessities.
2. If your product requires strong impact resistance, we recommend choosing the high-impact grade. This material is suitable for manufacturing helmets, car bumpers, etc.
3. If your product is used in electrical appliances and requires fire resistance, we recommend choosing the flame-retardant grade. This material is suitable for manufacturing security casings, smart switch panels, Wi-Fi routers, and some electronic casings.
4. If your product has high medical requirements, we recommend using the medical grade. This material is suitable for manufacturing hearing aid casings, blood analyzer casings and more.